20.6. Setup Examples¶
Your VT AIR’s High Availablity Feature can be configured and used based your needs. This page shows you different common example setups. The capabilities are not limited to these setups though. The three core components of VT AIR’s High Availability Feature are independent of each other and can be configured and used individually.
Configuration Synchronization
States Synchronization
VRRP Virtual IPs
(DHCP High Availability)
20.6.1. Configuration Synchronization only¶
This section describes a setup in which your VT AIR devices synchronize their configuration but do not provide automatic failover protection. This is for example useful if you are able to swap in a second VT AIR manually in case of a fault with your primary device. The configuration synchronization feature ensures that your secondary device’s configuration is always up to date.
Another scenario would be configuration synchronization in a common network across multiple sites. If you wish to keep parts of the configuration consistent across multiple sites without individually configuring each device, you can use the Configuration Synchronization Feature to do so.
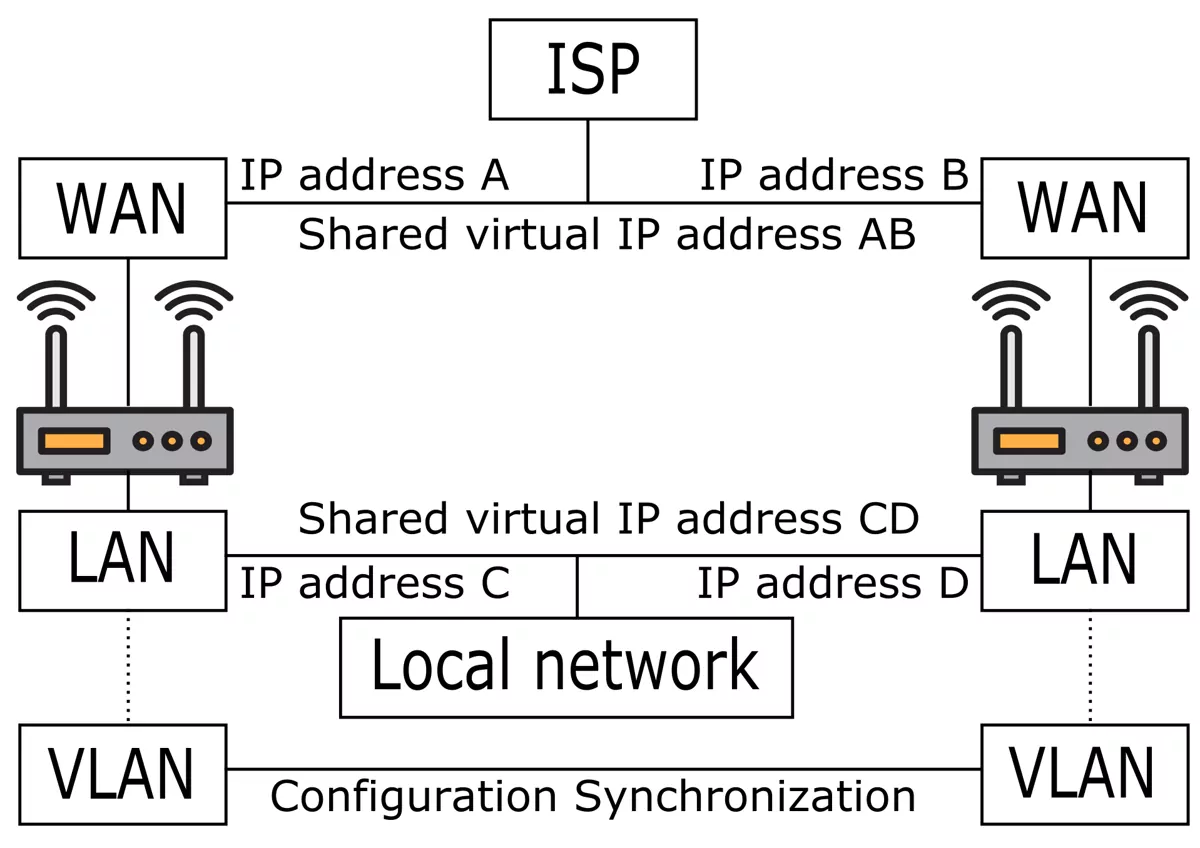
Refer to Configuration Sync for setup details. In a typical setup where your local network is connected to the LAN Interface you would create a VLAN on top of your LAN Interface with static IP addresses for your VT AIR devices. The devices then share their configuration via this VLAN. Alternatively you can use a seperate physical Interface for this.
20.6.2. Full Failover Setup¶
If you wish to have full automatic failover support you can configure your VT AIR devices to automatically synchronize their configuration and automatically switch to a backup device in case of a fault. This is for example useful for critical networks in remote locations that do not allow for significant downtime.
Refer to the paragraph above for details on how to configure the Configuration Synchroinization first. Also refer to DHCP High Availability if your VT AIR provides DHCP functionality to your network.
Each router gets its unique IP address in your local network. For an automatic failover setup the standard gateway and its IP address must not change suddenly during operation. Thus the standard gateway needs to be a virtual IP address that is shared between all the routers in your network. See VRRP Shared Virtual IP Address for configuration details. The same priciple also applies to the WAN Interface. In case a secondary device continues operation for the primary device the IP address must not change.
Note
Your VT AIR’s High Availability Feature might not be able to detect defective cables or causes outside of the device itself. It is only designed to register faulty devices and re-route traffic through a secondary device.