10.3. Configure Interfaces¶
In order to change an Interface setting in the system you need to navigate to Interfaces → INTNAME where INTNAME is the interface name you want to edit.
Depending on the underlying interface this represents you have different options and settings on this page.
On a normal Interface you have the following Settings.
10.3.1. General¶
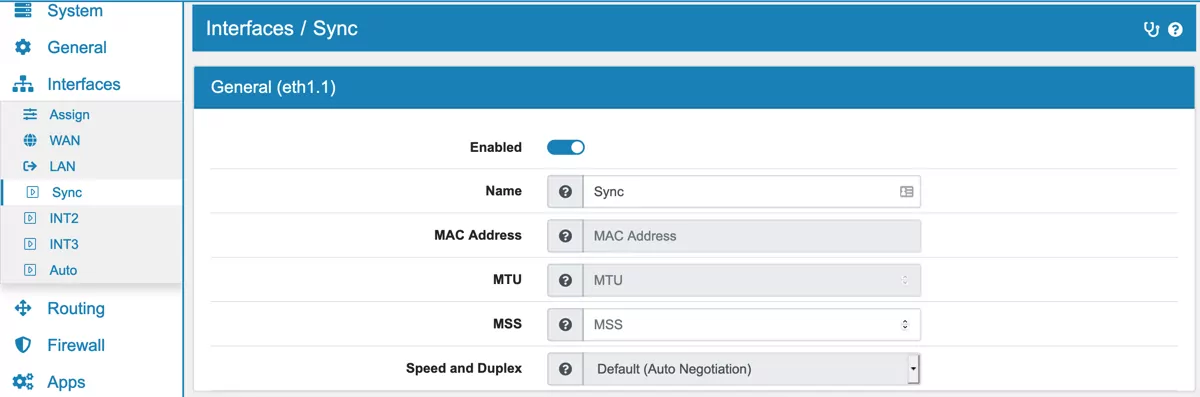
Enabled to enable or disable the interface
Name can be changed to any name you like. The Interface name is used throughout the GUI for example when defining Firewall rules that belong to this Interface. The name will also be displayed as ALTNAME in the shell for each interface.
MAC Address if you want to override the default MAC Address. Be aware that depending on the interface representation this can have consequences on other interfaces. For example all VLANs of an interface share the same MAC.
MTU will change the Maximum Transition Unit. It is 1500 per default and if you plan on using IPv6 the minimum can not be less than 1280.
MSS fix will clamp the TCP connection at this size. It is usually only needed with PPPoE and PPP and on those interfaces it is generated by default.
Speed and Duplex configures whether the connection speed is automatically negotiated on the Interface. Alternatively you can also manually select a desired speed (within the limits of your hardware). On some Interface types like VLANs this option is grayed out since the connection speed depends on the underlying (physical) Interface.
10.3.2. IPv4 Settings¶
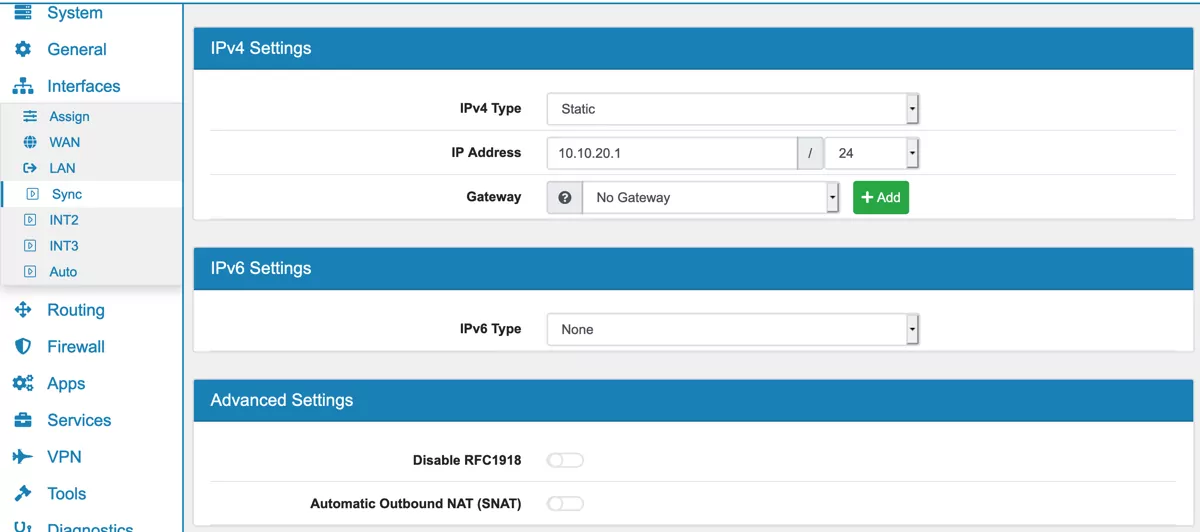
IPv4 settings contain the IPv4 type.
All IPv4 types are:
None
Static
DHCP
PPP
PPPoE
Depending on the interface you only see a subset of the available options.
DHCP will use the DHCP Client to get an IP Address and Gateway on the Interface.
Static lets you configure an IP Address and if applicable a Gateway manually.
Gateway is available for static IPs and only affects the IP Addresses of the VT AIR itself. The IP Addresses of the VT AIR will always use this Gateway. This is especially needed in a multi WAN Setup so that the interface IP Address is responsive if the default route is with another interface. Otherwise all routing decisions are based on the main routing table, also for interface IP Addresses.
Lease Time is the DHCP Maximum Lease Time in seconds and is available if the IPv4 type is DHCP. The DHCP address will be refreshed after this time. If this is an Cellular interface a low value is necessay in case the Cellular connections changes.
10.3.3. IPv6 Settings¶
IPv6 settings contain the IPv6 type.
All IPv6 types are:
None
Static
DHCP
SLAAC
Track
Depending on the interface you only see a subset of the available options.
Static lets you configure an IP Adress and if applicable a Gateway manually.
DHCP will use the DHCP Client to get an IP Address. This requires a Router that advertises itelf with RA. IA_NA can be set manually otherwise one will be generated. That is needed to obtain an IP Address from the server. Prefix Delegation can be enabled to also obtain a Prefix from the DHCP Server that can then be set on other interface via Track. IA_PD can be set manually. That is needed to obtain an IP Address from the server. Prefix Delegation Size is auto by default. You can also set the size of the prefix you want to request.
SLAAC will get the IP Address with the IPv6 SLAAC mechanism. Make sure there is at least one IPv6 Router that advertises itself in the network.
Track will obtain an IP Address via Prefix Delegation from another Interface. Please also select the interface that obtains a prefix. IPv6 Prefix ID If the ISP has delegated more than one prefix via DHCPv6, the IPv6 Prefix ID controls which of the delegated /64 subnets will be used on this interface. For example, If a /60 delegation is supplied by the ISP that means 16 /64 networks are available, so prefix IDs from 0 through 15 may be used.
Router Advertisement (Client) will either obtain the IP Address if SLAAC is enabled and/or the Gateway. The Gateway in IPv6 is always obtained by the Router Advertisement mechanism even if DHCP is used. If you disable Router Advertisement this mechanism will be disabled.
Gateway is available for static IPs and only affects the IP Addresses of the VT AIR itself. The IP Addresses of the VT AIR will always use this Gateway. This is especially needed in a multi WAN Setup so that the interface IP Address is responsive if the default route is with another interface. Otherwise all routing decisions are based on the main routing table, also for interface IP Addresses.
10.3.4. Advanced Settings¶
Disable RFC1918 will automatically create a Firewall rule to block all IPs in the RFC1918 block. Have a look at Builtin Network Ranges for a description of RFC1918. These IP addresses are used in private networks and it may be useful to block them from communicating on the WAN Interface for example.
Automatic Outbound NAT (SNAT) will automatically create a SNAT rule for this interface.
Note
Pay special attention to this if you have a High Availability setup. It might be required for you to disable this option on your WAN Interface and manually set it up as described in HA Outbound NAT.
Automatic DDoS Limiting will create a rule to limit connections per incoming host per minute. The number of connections per minute can be set in the global settings.
MPLS enables MPLS. It is disabled by default.
VRF lets you choose a VRF. It is disabled by default.
10.3.5. WIFI Client¶
In case the interface is a wifi interface you can set the SSID and Password in order to join a wifi network.
10.3.6. WPA Authentication (802.1X)¶
WPA Authentication (802.1X) can be enabled by selecting a Protocol. The following protocols are available:
EAP-TLS
EAP-PEAP/MSCHAPv2 (both PEAPv0 and PEAPv1)
EAP-PEAP/TLS (both PEAPv0 and PEAPv1)
EAP-PEAP/MD5-Challenge (both PEAPv0 and PEAPv1)
EAP-TTLS/EAP-MD5-Challenge
EAP-TTLS/EAP-MSCHAPv2
EAP-TTLS/EAP-TLS
EAP-TTLS/MSCHAPv2
EAP-TTLS/MSCHAP
EAP-TTLS/PAP
EAP-TTLS/CHAP
EAP-MD5-Challenge
EAP-MSCHAPv2
Entering an Anonymous Identity is optional. For authentication purposes an Identity and Password are required.
When selecting a protocol which supports PEAP or TTLS a Certificate Authority and Certificate are needed.
Note
The command line utility wpa-cli can be used to get information about the WPA Authentication status. It is also possible to create event driven commands on authentication or deauthentication. Please contact us if you need assistance in that regard.