10.15. VXLAN¶
You can find the VXLAN Settings at Interfaces → Assign → VXLAN.
Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) is a network virtualization technology that attempts to address the scalability problems associated with large cloud computing deployments. It uses a VLAN-like encapsulation technique to encapsulate OSI layer 2 Ethernet frames within layer 4 UDP datagrams. VXLAN endpoints, which terminate VXLAN tunnels and may be either virtual or physical switch ports, are known as VXLAN tunnel endpoints (VTEPs)
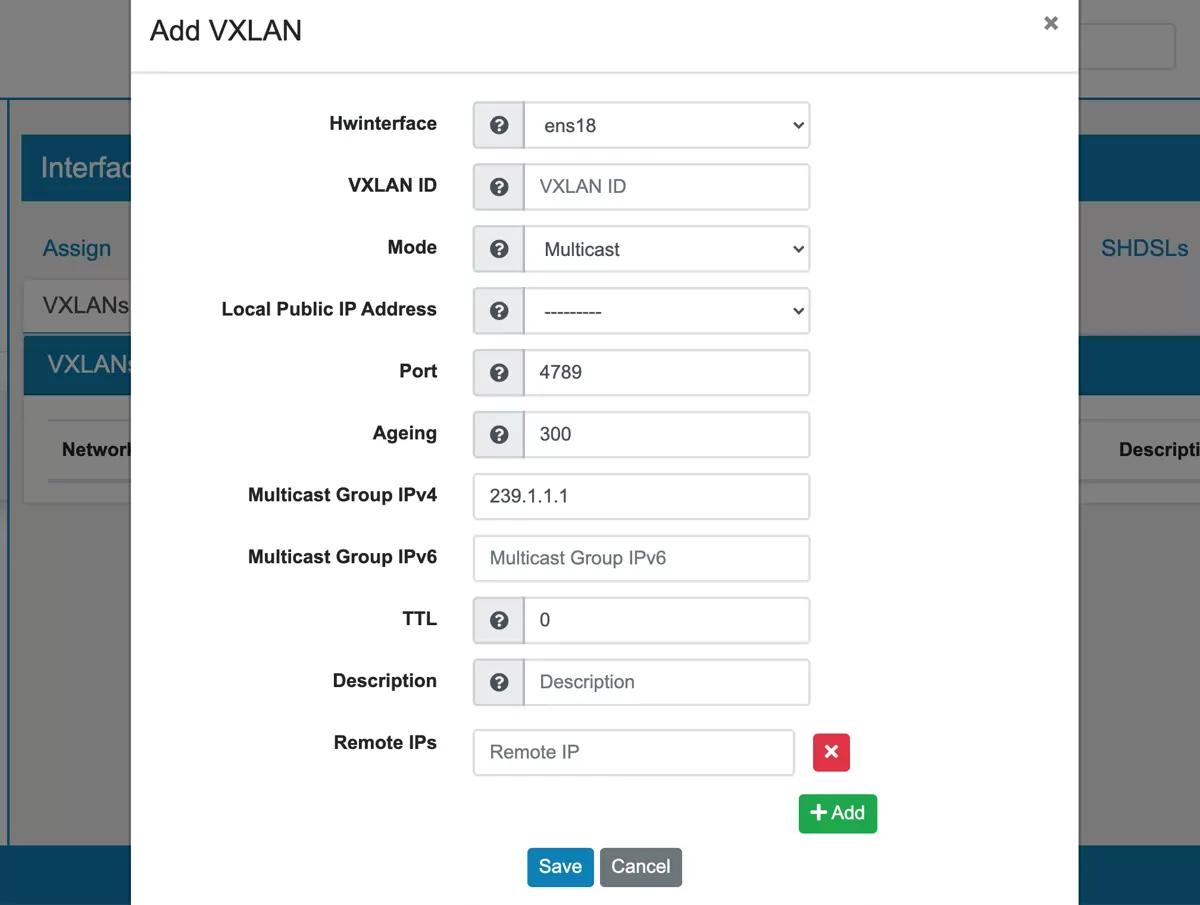
VXLANs can only be configured on top of Physical Interfaces.
HWInterface is the underlying interface.
VXLAN ID has to be unique to identify the VXLAN.
Mode Multicast or Head End Replication. Multicast is more effecient but it has to be configured on all VTEPs. The Multicast group must be same. Head End Replication replicates all entries to all VTEPs.
Local Public IP Address that is used as the sender to connect to other VTEPs. If none is provided one will be auto used from the underlying HWInterface.
Port to use to connect to VTEPs and receive connections.
Ageing The vxlan keeps track of ethernet addresses seen. This is the timeout in seconds for members that have not been seen. Between 0 and 4096. Default is 300
Multicast Group v4 Multicast Group IPv4 Multicast Group v6 Multicast Group IPv6. One of them is enough for a Multicast Setup.
TTL Specifies the TTL value to use in outgoing packets. Between 0 and 255, 0=auto
Remote IPs remote VTEPs to connect to.
VXLANs can also be used in Bridges.