17.6. DHCP & RA¶
You can find the DHCP & RA Settings at Services → DHCP & RA.
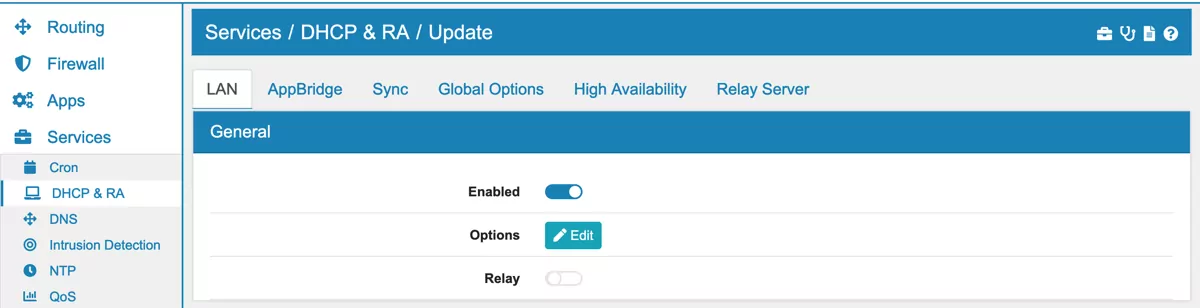
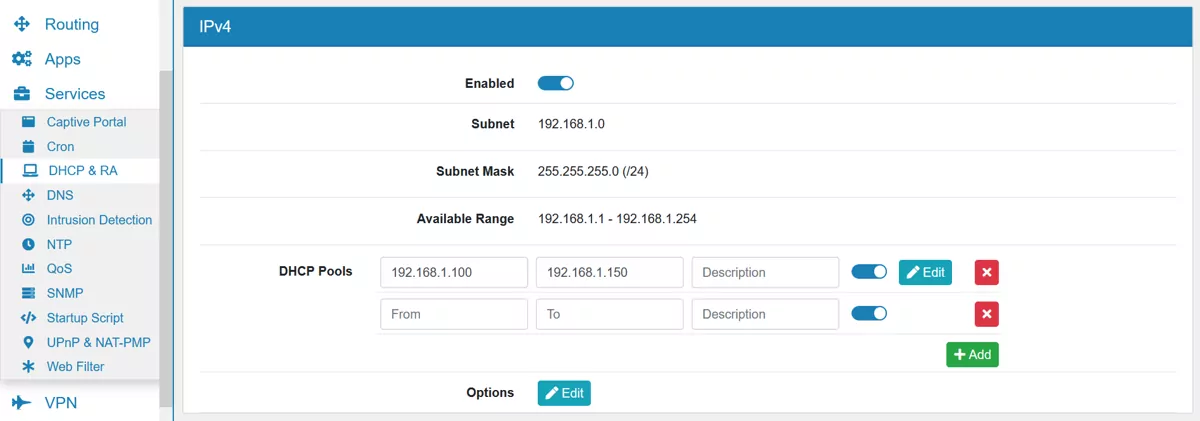
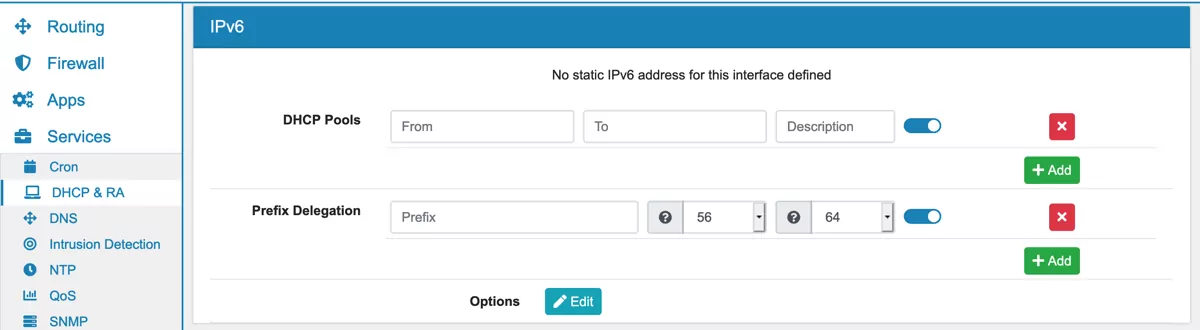
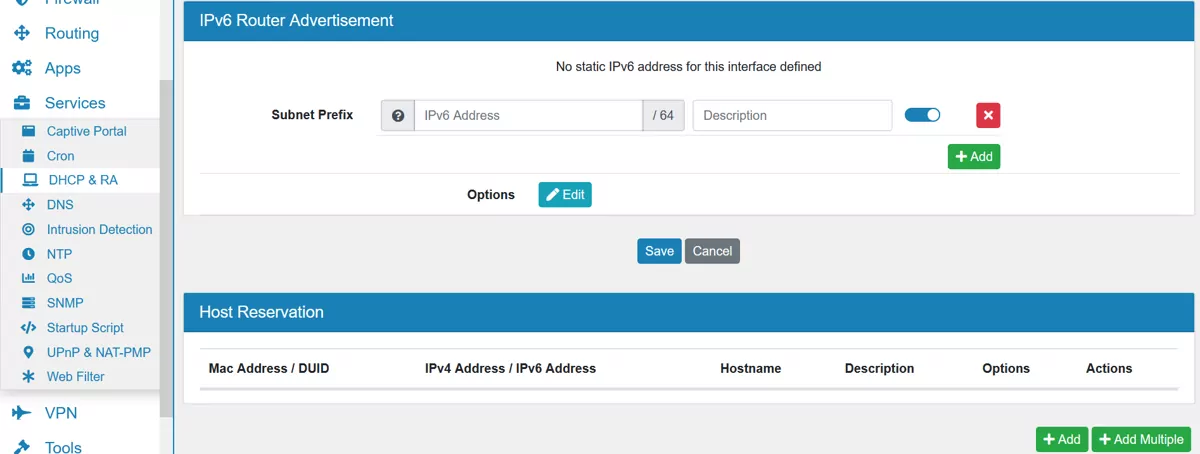
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is used to dynamically assign an IP address and other network configuration parameters to other devices on the network so they can participate in the network communication.
You can export the settings in the top right corner as an Excel spreadsheet.
Each interface has an own tab where DHCP can be enabled individually. IP protocol v4 and v6 need to be enabled and configured separately. An interface needs a static IP address to be configurable. Multiple DHCP Pools can be set up, but each one needs to be in the Available Range and they cannot intersect each other. The options are hierarchically and overwritten by the lower ones. This means that the DHCP Pool options overwrite IP protocol options, the IP protocol options overwrite the interface options and the interface options overwrite the general options.
17.6.1. Network Booting¶
The functionality of Network Booting can be found in the general options of each interface. When enabled, you can configure a TFTP Server, Next Server and a file name path for Default BIOS, iPXE, UEFI 32 bit and UEFI 64 bit.
17.6.2. MAC and DUID Deny¶
The functionality of MAC Deny can be found in the v4 options and the DUID Deny can be found in the v6 options of each interface. The MAC and DUID can both be a complete address or a partial address. Clients with their address configured here will be ignored by the DHCP server and will not get a lease.
17.6.3. Extra Options¶
Additionally to the DHCP options there are a lot of Extra Options which can be found in the v4 and v6 options of each interface. There are 254 different options to choose from but duplicates are not allowed. For the predefined options the data type is fixed, whereas for the rest it can be selected individually. All options are forcible set and send with each DHCP packet.
17.6.4. Relay Server¶
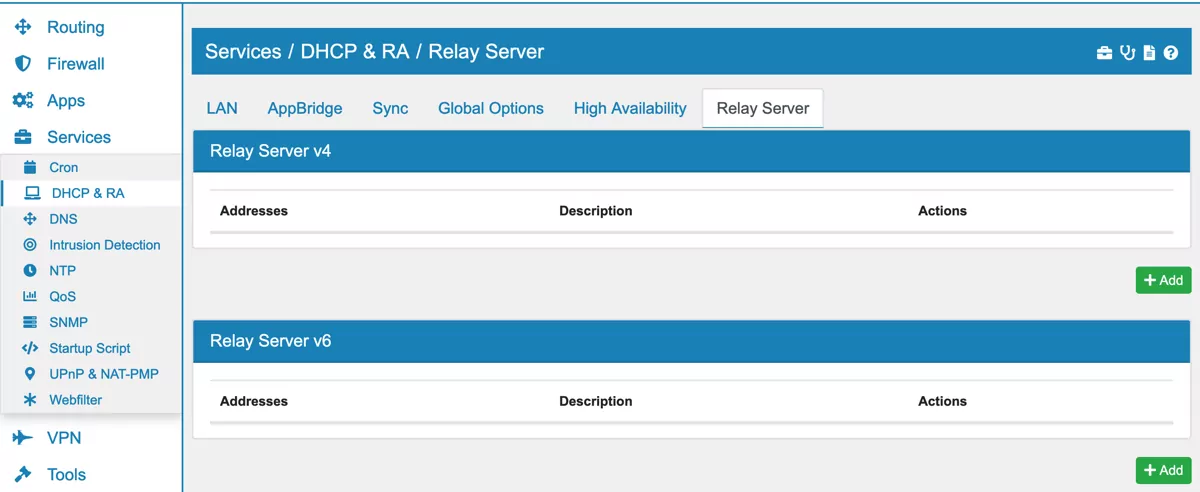
If a DHCP server already exists in the network you can put it here, so devices will get its information from this DHCP server instead. The DHCP requests will be forwarded to this server. You need to activate the Relay Server on each Interface Tab in the DHCP Settings. You can then choose a Relay Server v4.
17.6.5. IPv6 Router Advertisement¶
With Router Advertisement the router advertises its presence in the network for an IPv6 network. A static IPv6 address needs to be set up on the interface to use this functionality. There are four Modes: Router Only, SLAAC, DHCP and Both. Multiple Subnet Prefixes can be added by an IPv6 address. It’s also possible to configure several options which are similar to the DHCP ones.
17.6.5.1. Router Only¶
Is advertising the presence of VT AIR as a router for the network interface. The static Interface IPv6 is used for this.
17.6.5.2. SLAAC¶
A router is advertised and a prefix as well so the client can configure his IPv6 address automatically.
17.6.5.3. DHCP¶
A router is advertised and also the option that the client should contact a DHCP Server for an IPv6 address.
17.6.5.4. Both¶
A router is advertised and also SLAAC as well as DHCP.
17.6.6. IPv6 Prefix Delegation¶
IPv6 Prefix Delegation is used to assign a network address prefix and automate configuration and provisioning of public routable addresses for a network. A static IPv6 address needs to be set up on the interface to use this functionality. Multiple Prefix Delegations can be added by an IPv6 address as Prefix, a Prefix Length and a Prefix Delegation Length. The Prefix Delegation Length must be greater or equal to the Prefix Length. The Prefix can’t intersect with an already used IPv6 Pool.
17.6.7. Host Reservation¶
Multiple Host Reservation can be created with a MAC Address, Hostname and IP Address. For IPv4 you can specify a Client Identifier and for IPv6 you can specify a DUID (DHCP Unique Identifier).
The Client Identifier can be used if there is no MAC Address for IPv4. The options are mutually exclusive. The DUID is also preferred over the MAC Address for IPv6 reservations.
The advanced options are identical to the previous DHCP options.
Each Host Reservation creates a Network Object that can be used in the Firewall Rules. If you delete the Host Reservation, you will need to remove it from the Firewall Rules first. A list of all active Firewall Rules that include the Host Reservation will be shown on the delete action as a warning.