17.10. Intrusion Detection¶
You can find the Intrusion Detection Settings at Services → Intrusion Detection.
The Intrusion Detection is using Suricata, an open source-based intrusion detection system (IDS) and intrusion prevention system (IPS).
17.10.1. General Settings¶
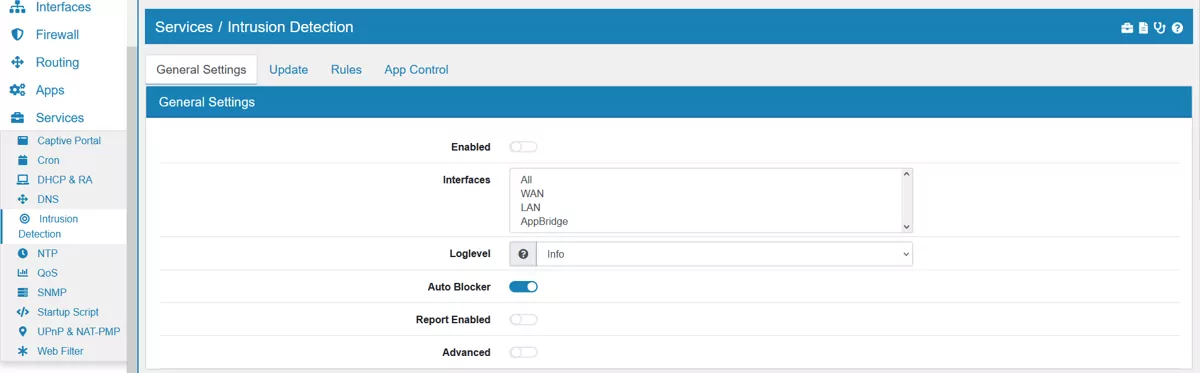
On this page Suricata can be enabled or disabled.
The Mode can be IDS (Intrusion Detection System), IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) or IDS & IPS.
One or more Interfaces can be selected where traffic should be analyzed by Suricata.
Disable for Internal Traffic will disable Intrusion Detection for private network IPs. This will make it faster for internal traffic while securing internet facing traffic.
Loglevel for Suricata can be setup and is Info by default.
Auto Blocker will block IP Adresses that were matched by a security event rule.
Note
Only IPs that are not in the Home Networks and from one of the following categories will be blocked for 60 seconds: - Attempted Denial of Service - Denial of Service - A Network Trojan was detected - Detection of a Denial of Service Attack - Web Application Attack - Exploit Kit Activity Detected - Successful Credential Theft Detected - Crypto Currency Mining Activity Detected - Malware Command and Control Activity Detected
Report Enabled can be enabled or disabled. If it is enabled you can define a Report Email that should receive reports. Make sure to configure an Email server in the settings. The report will contain information about alerts and blocked events in the given period.
The option Advanced allows the usage of Pass Last and Custom Options.
Pass Last will change the order of rule execution. Usually Pass rules are evaluated before drop rules.
IPS Check Firewall will also monitor all traffic coming and going from the VT AIR itself. Be aware that this might block traffic to the GUI or services on the Firewall. The default is off, it is better to use good Firewall Rules to protect the VT AIR itself.
IPS on Bridge will also monitor all traffic passing through all configured Bridges on the Layer 2 level. This will only affect traffic, that is not filtered by the firewall in a VLAN or another type of interface that is on top of the Bridge.
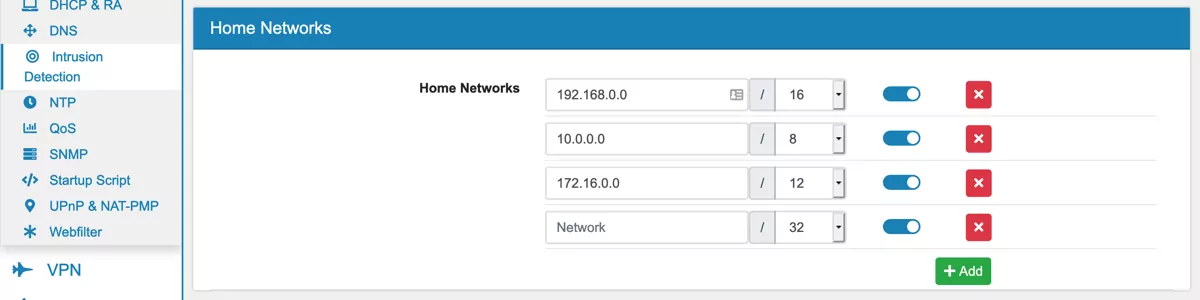
Multiple Home Networks can be added with their ip address and port. By default the networks 192.168.0.0/16, 10.0.0.0/8 and 172.16.0.0/12 are created. Home Networks are often used in the default rules to identify internal and external traffic and to apply different rules.
You can export the settings in the top right corner as an Excel spreadsheet.
17.10.2. Performance Settings¶
Intrusion Detection performance heavily depends on memory settings.
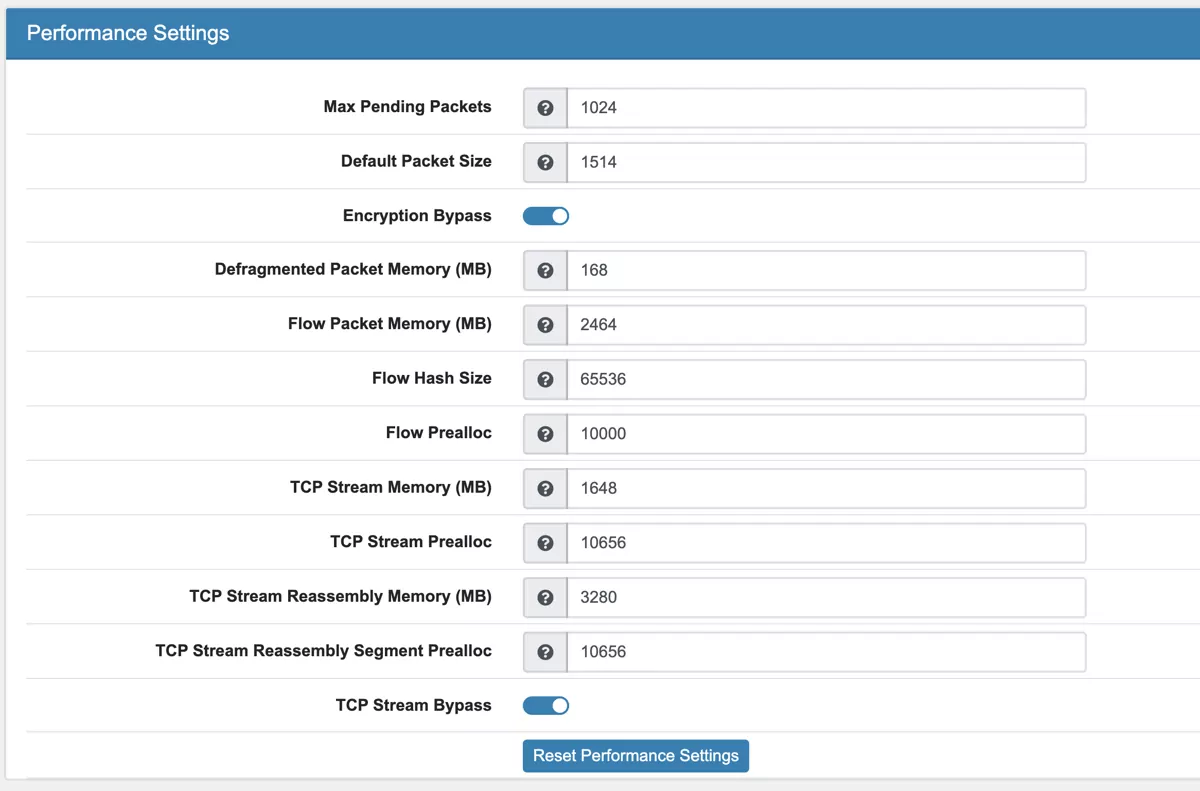
Max Pending Packets This can range from one packet to tens of thousands/hundreds of thousands of packets. It is a trade of higher performance and the use of more memory (RAM), or lower performance and less use of memory. A high number of packets being processed results in a higher performance and the use of more memory. A low number of packets, results in lower performance and less use of memory.
Default Packet Size With the default-packet-size option, you can set the size of the packets on your network. It is possible that bigger packets have to be processed sometimes. The engine can still process these bigger packets, but processing it will lower the performance.
Encryption Bypass Encrypted traffic has very little information for IPS. With this option it will be offloaded after initial inspection which leads to a huge speedup and frees resources to process more packets.
Defragmented Packet Memory (MB) Maximum memory to use to reassembly defragment packets.
Flow Packet Memory (MB) Maximum amount of bytes the flow-engine will use. More memory will result in faster processing.
Flow Hash Size Higher Hash size gives better performance but needs more memory.
Flow Prealloc To mitigate the engine from being overloaded, this option instructs Suricata to keep a number of flows ready in memory.
TCP Stream Memory (MB) Maximum amount of bytes the tcp stream engine will use. More memory will result in faster processing.
TCP Stream Prealloc Sessions prealloc per stream thread
TCP Stream Reassembly Memory (MB) Maximum amount of bytes the tcp stream reassembly engine will use. More memory will result in faster processing.
TCP Stream Reassembly Segment Prealloc Reassembly Segment prealloc per stream thread
TCP Stream Bypass The bypass option activates ‘bypass’ for a flow/session when either side of the session reaches its depth. Bypass can lead to missing important traffic. It is still enabled by default as it leads to speedups.
Reset Performance Settings will calculate a general value based on available memory ressources for each option. You can tweak the values if your setup requires different settings.
17.10.3. Update¶
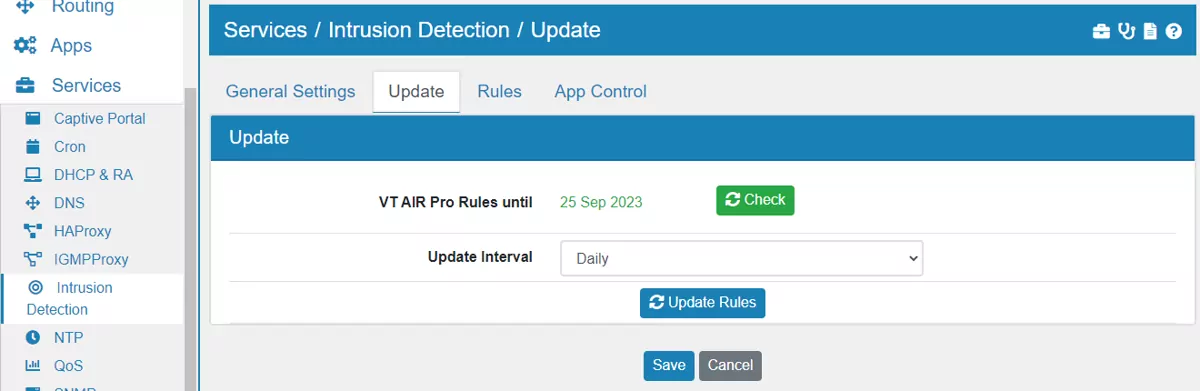
Here you can configure see the rules that are used. If you purchased * VT AIR Pro Rules** your device will pull the licence from the VT AIR Portal* and you can see the licence and expiration date here. If not the ETOpen Emerging Threats rules will automatically be activated instead.
The VT AIR Pro Rules* already include the ETOpen Rules.
Update Interval is a cronjob which will update the rules according to the selected time interval.
Be aware that the more rules you select the slower Suricata gets. It might be advisable to only use rules and categories that you need.
17.10.4. Rules¶
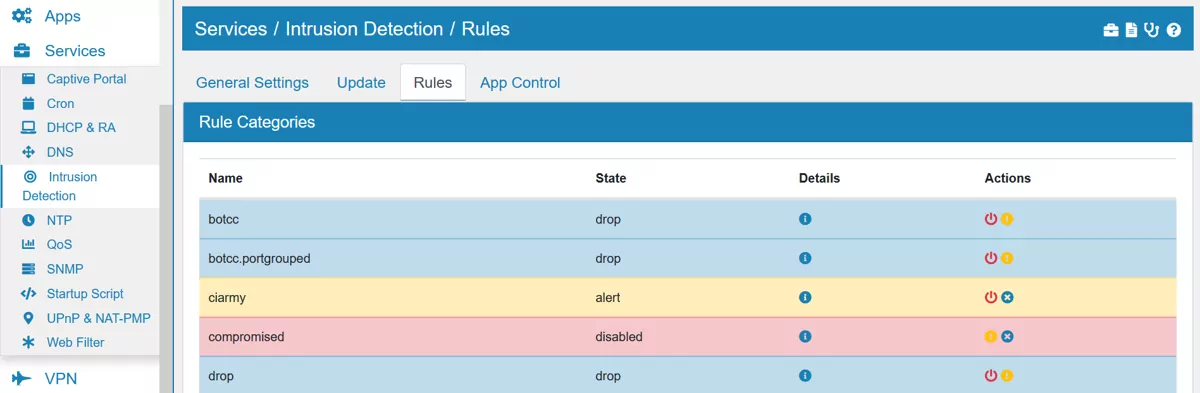
Here you can see all installed and used rule files which ususally correspond to a single category. You can click on the detail icon of each rule to see the specific definion of it. Each rule file can be disabled, set to alert or drop on the actions column on the right side. Below the list there are also three buttons to change all rules at once: Drop All, Alert All and Disable All.
Multiple SIDs can be added to disable specific rules by their Signature ID.
At the bottom you can add Custom Rules.
17.10.5. Example Suricata Configuration¶
In your VT AIR’s software you get to choose between two rule packages that you can enable. Each set of rules is divided into different categories. Based on these categories you can specify in greater detail what kind of traffic you want to be blocked. Not all of these might be desireable under all circumstances.
By default Suricata creates its own set of rules. These can be found here.
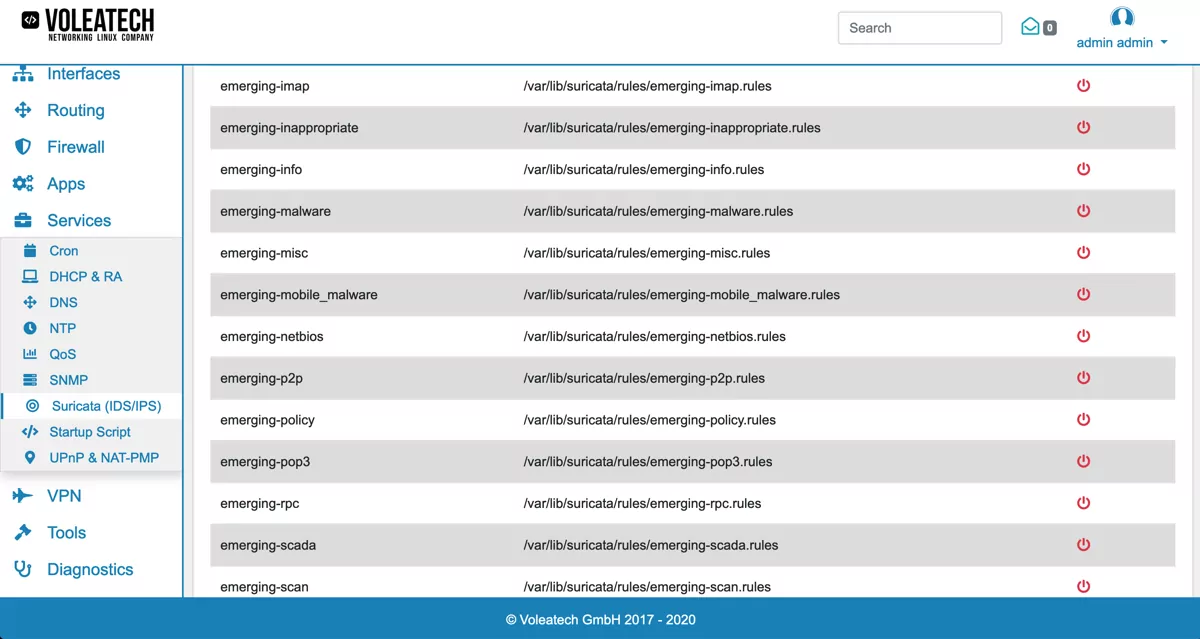
When enabling the Emerging Threats Open Rules they will be shown to you as emerging-XXX under Services → Suricata → Rules. A detailed description of the different categories can be found in the official documentation.
We recommend to set the Interfaces to any and create a firewall rule to only filter relevant traffic. As a recommendation you should create a Global Firewall Rules (Forward and Input) with Input Interface Any, Output Interface Any, the Action Match, Source Private Networks, Destination Private Networks and under Advanced Settings set the option Bypass IDS/App Control. The rule should be the first user created rule under the Global Rules.